1. What is a VPC?
VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) is your own isolated network inside AWS. Think of it as a virtual version of your home network. Just like your home has rooms, a VPC has subnets, and just like your home has doors and hallways to go outside, AWS uses route tables and gateways to control network traffic.
- Key points about VPCs:
- It’s isolated from other AWS accounts.
- You define the IP address range (CIDR block), e.g.,
10.0.0.0/16. - Acts as a container for subnets, route tables, gateways, and security controls.
2. Subnets – Dividing Your VPC
A subnet is a segment of your VPC’s IP address range. Think of it as a room in your house. Subnets allow you to organize resources, control traffic, and define access rules.
- Types of subnets:
- Public Subnet – Accessible from the internet. Typically for web servers.
- Private Subnet – Not accessible directly from the internet. Typically for databases or internal services.
- Example:
If your VPC has a CIDR block10.0.0.0/16, you could create:- Public subnet:
10.0.1.0/24 - Private subnet:
10.0.2.0/24
- Public subnet:
3. Route Tables – Directing Traffic
A route table is like a map for traffic. It tells your network where to send traffic.
- Every subnet must be associated with a route table.
- A route table has rules called routes:
Destination: Where the traffic wants to go (IP range)Target: Where the traffic should be sent (gateway, NAT, peering, etc.)
Example:
- For a public subnet: traffic to
0.0.0.0/0(anywhere) → Internet Gateway - For a private subnet: traffic to
0.0.0.0/0→ NAT Gateway (to reach internet indirectly)
4. Internet Gateway – Connecting to the Internet
An Internet Gateway (IGW) is your VPC’s doorway to the internet. Without it, instances in your VPC cannot communicate with the outside world.
- Key points:
- Needed for public subnets to access the internet.
- Works with route tables to direct traffic from your subnet to the internet.
- AWS automatically assigns public IPs to instances in a public subnet (if enabled).
5. Putting together all
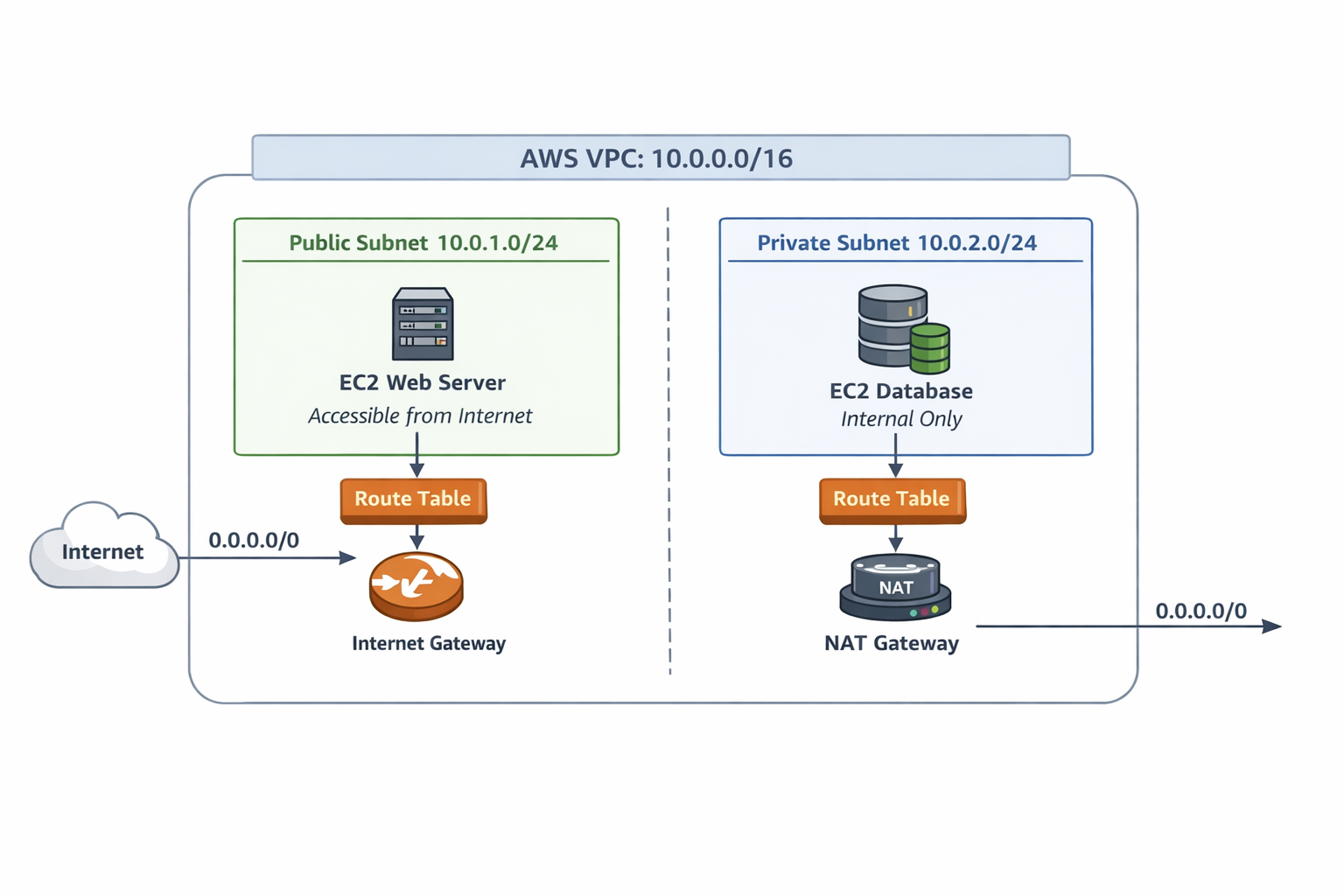
Let’s visualize a simple setup:
- Public subnet has direct internet access via the Internet Gateway.
- Private subnet can access the internet indirectly (for updates) via a NAT Gateway but isn’t exposed publicly.
- Route tables control how the traffic flows.
- Security groups and NACLs add extra layers of access control.
6. Why This Matters in Cloud & DevOps
- Security: Keep sensitive workloads in private subnets.
- Scalability: Organize workloads across multiple subnets for high availability.
- Flexibility: Route tables let you connect VPCs with other VPCs, data centers, or services.
Thankyou :)!